Hi everyone
After christmas, I had some time to improve my lab a little bit.
I decided to setup a Pi-Hole to use it as my main DNS and filtering app, and why not, use it also over my VPN with WireGuard , and be able to use it all the time reaching my Server from anywhere with a FQDN instead of an IP (Dynamic), with DuckDNS.
As a base system, I chose Ubuntu Server, with the minimum installation,
choose your own, maybe you will need to adapt some commands or content.
After login into my clean ubuntu server machine, and update all the packets,
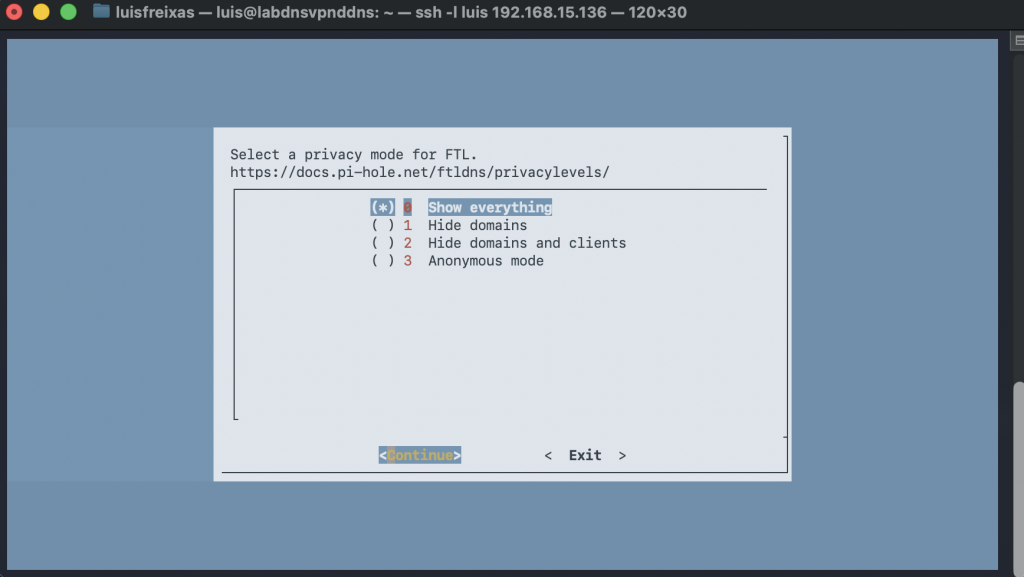
I went to the Pi-Hole website, and click into the Install Pi-Hole button.
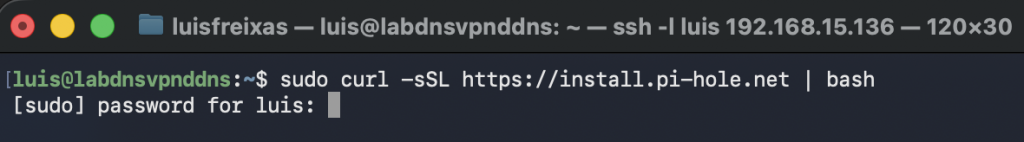
I used the Curl command with sudo before:
curl -sSL https://install.pi-hole.net | bash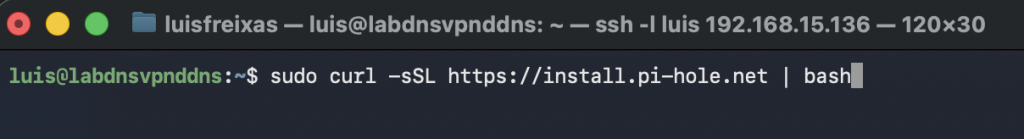


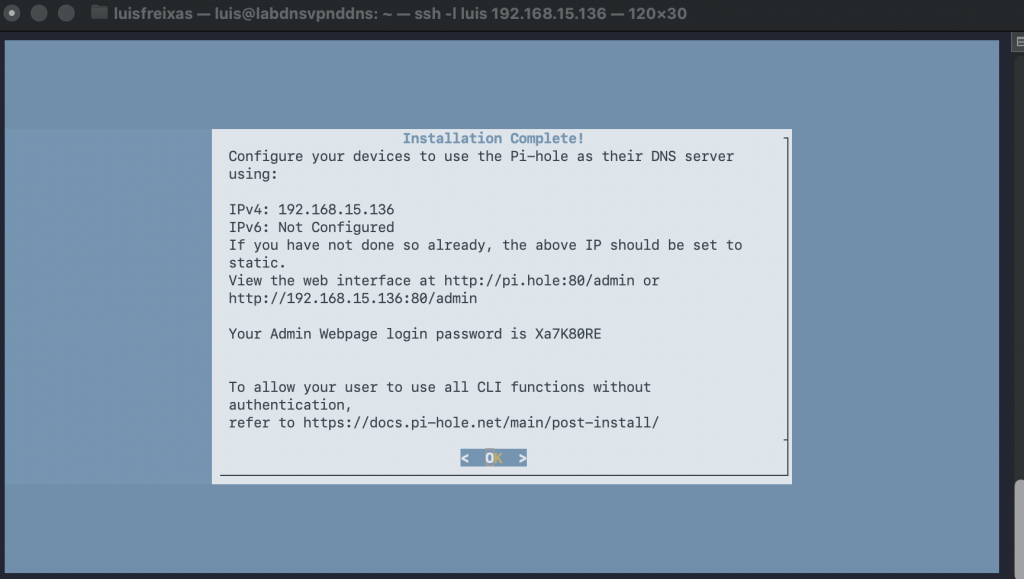
Now let´s open a browser and login into the Pi-Hole console:
http://192.168.15.136:80/admin
using the password provided in the previous step: Xa7K80RE
Done!
Now, let`s create our DuckDNS Sub domain before continuing:
Go to the DuckDNS website, and create an account, is free.

In my personal use case, I sing in with google, so the creation was super easy and smooth.
In the page, write down the name you want to use in your subdomain, and click in add domain

In my case, I have two domains created, im showing you them right now:
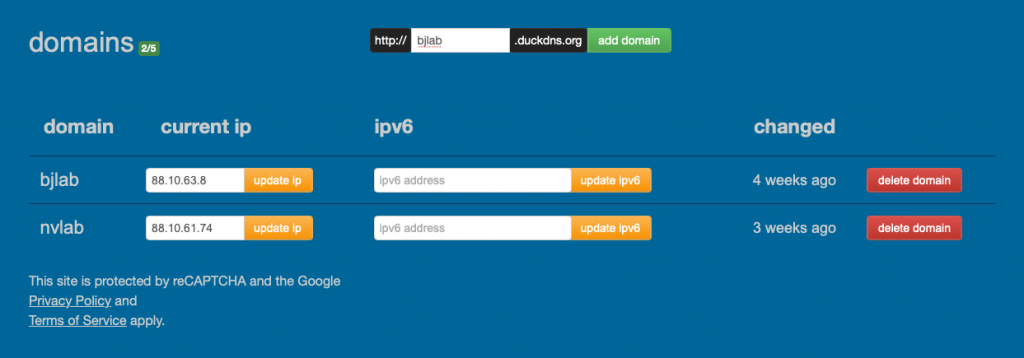
now, is time to connect our duckdns domain with our server to get the automatic IP update every time our dynamic IP address changes:
On top of the DuckDNS website, you will find an Install menu, click on it:
Follow the web instructions, choose your OS and setup, and follow the steps and input the information in your server, in my case, Linux base with cron tab:
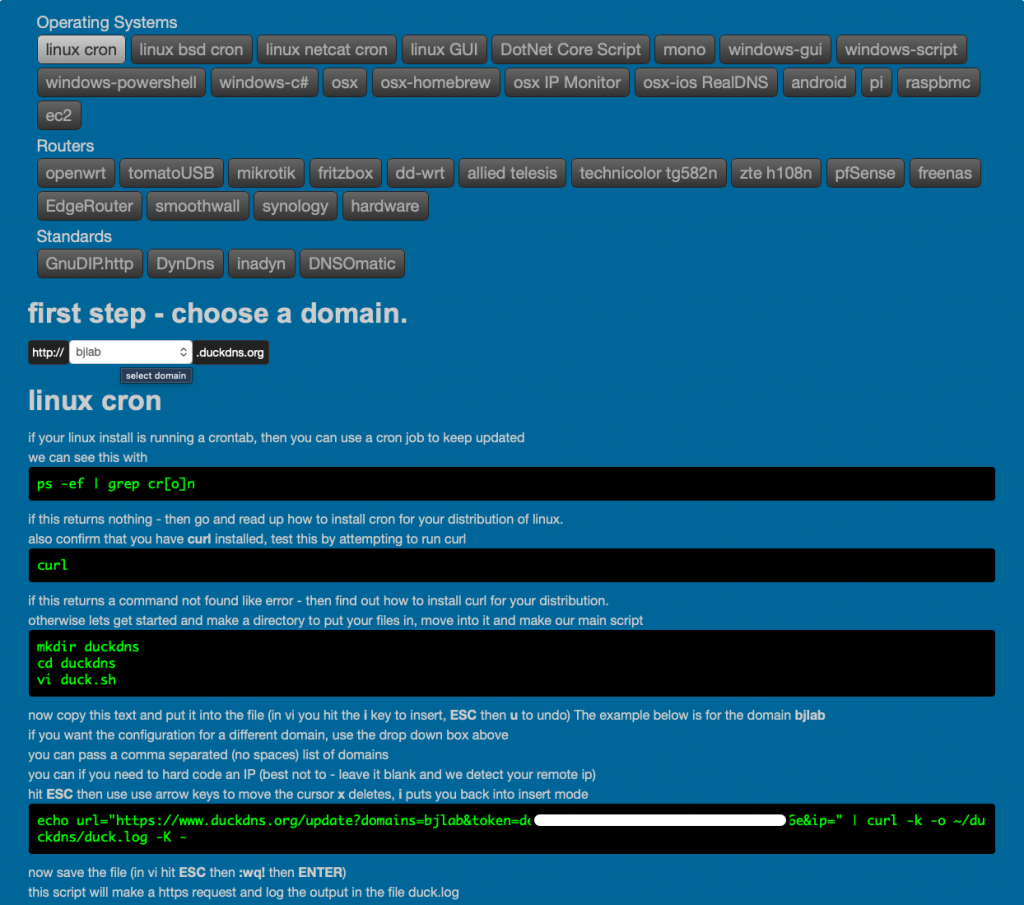
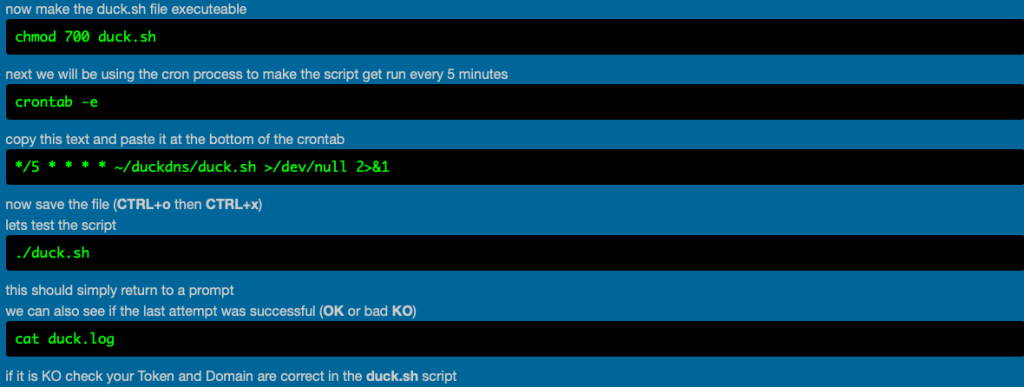
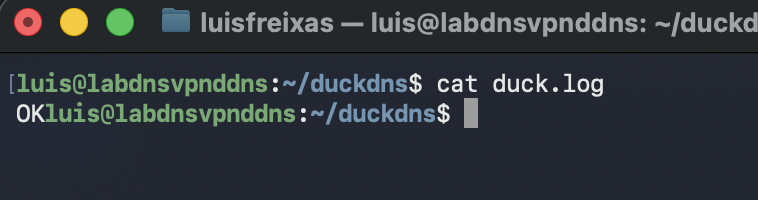
DuckDNS setup completed,
Now, Let´s install WireGuard
to be full set,
We are going to use this command, its awesome and prepared for raspberry pi, but also work with many distros and platforms, making the deployment super easy and smooth!
Follow the screenshots!
sudo curl -L https://install.pivpn.io | bash
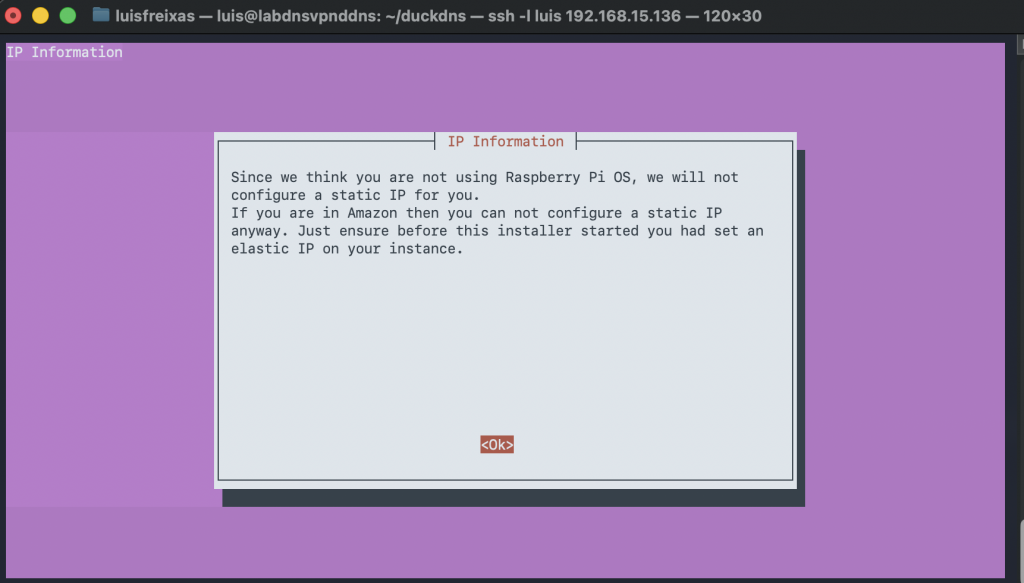
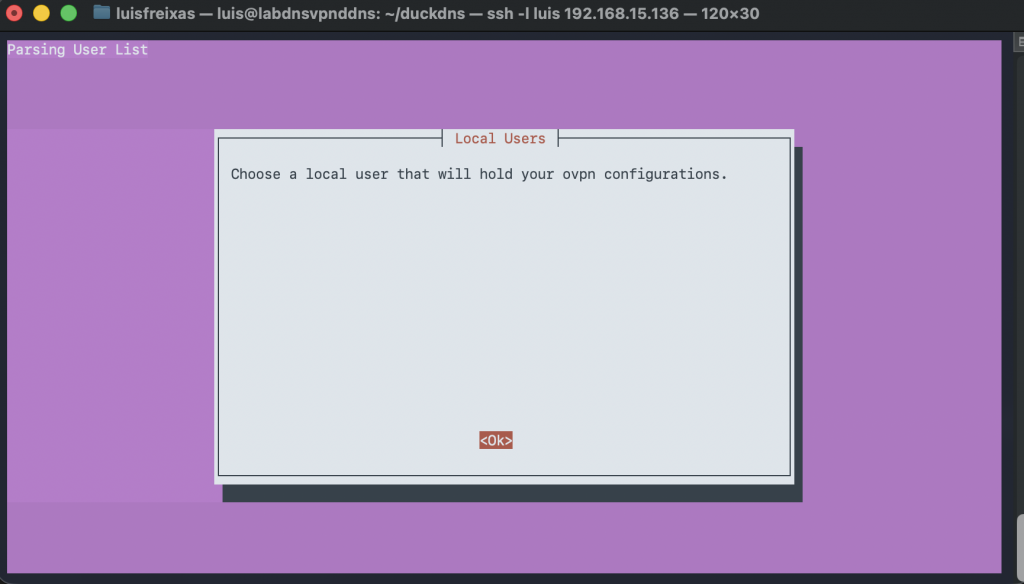
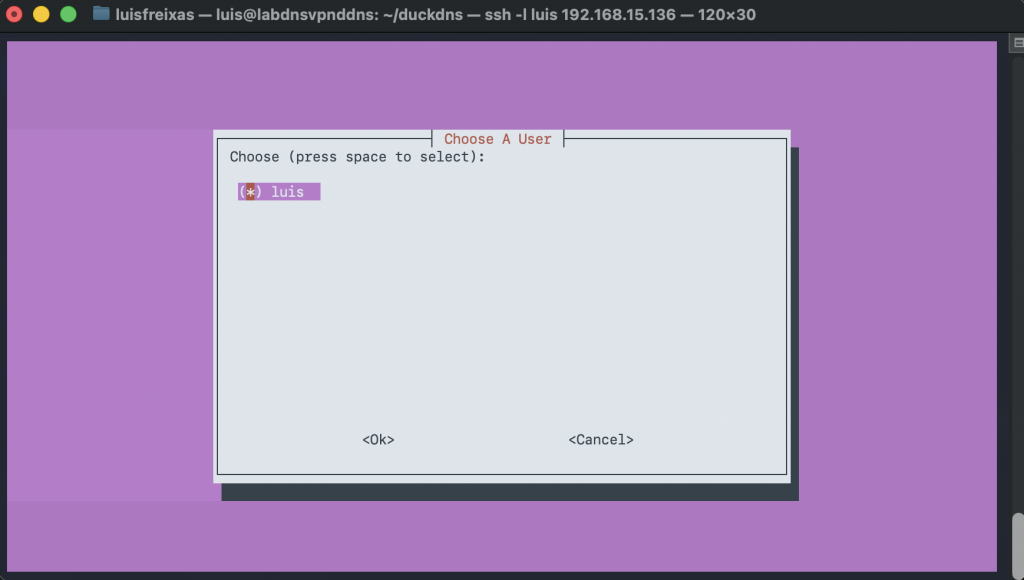
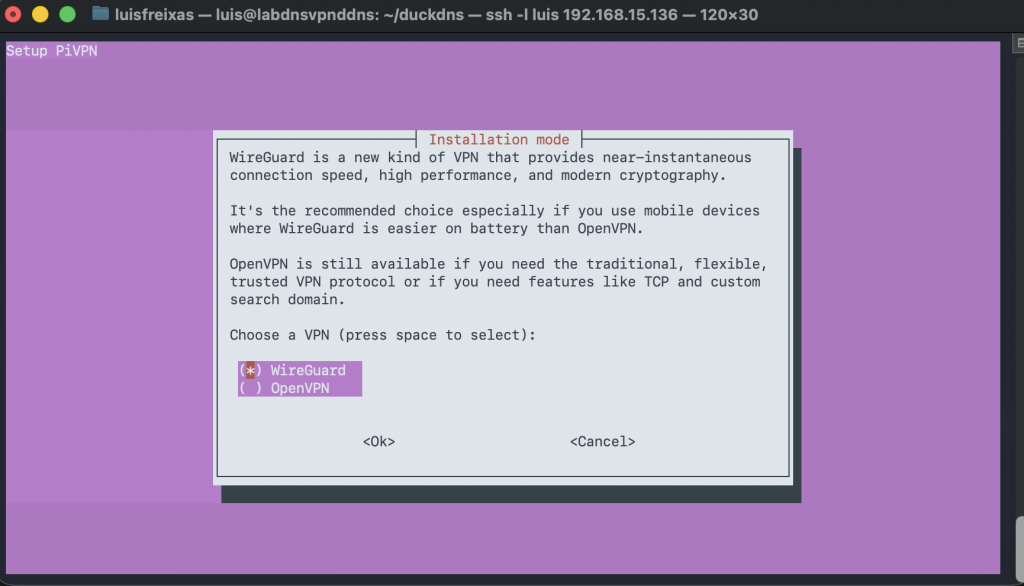
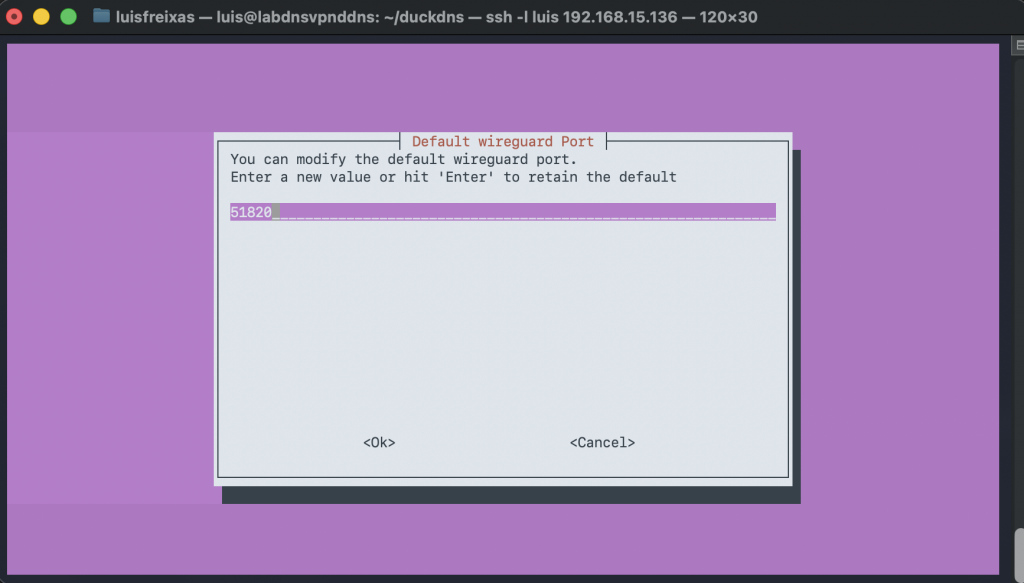
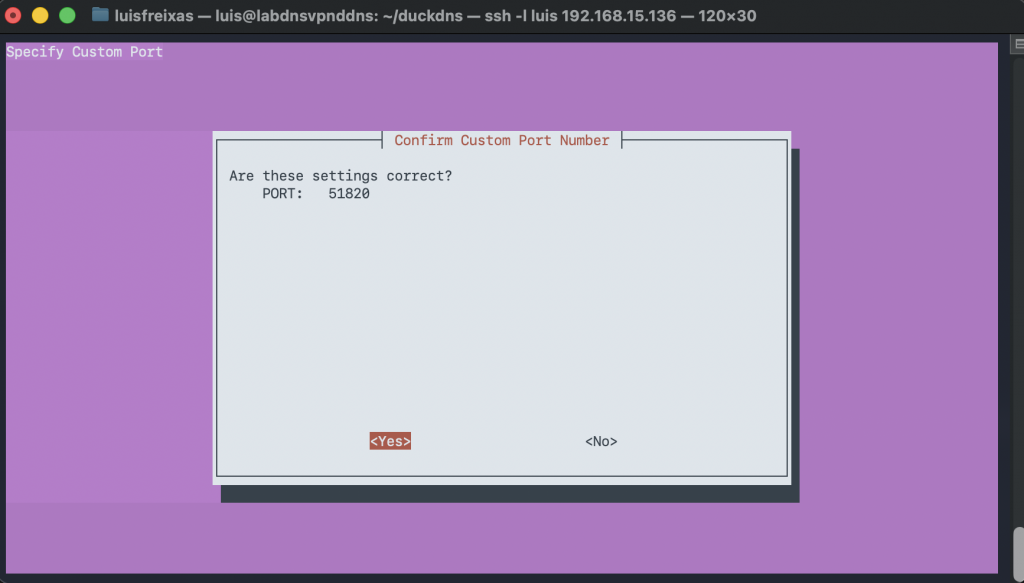
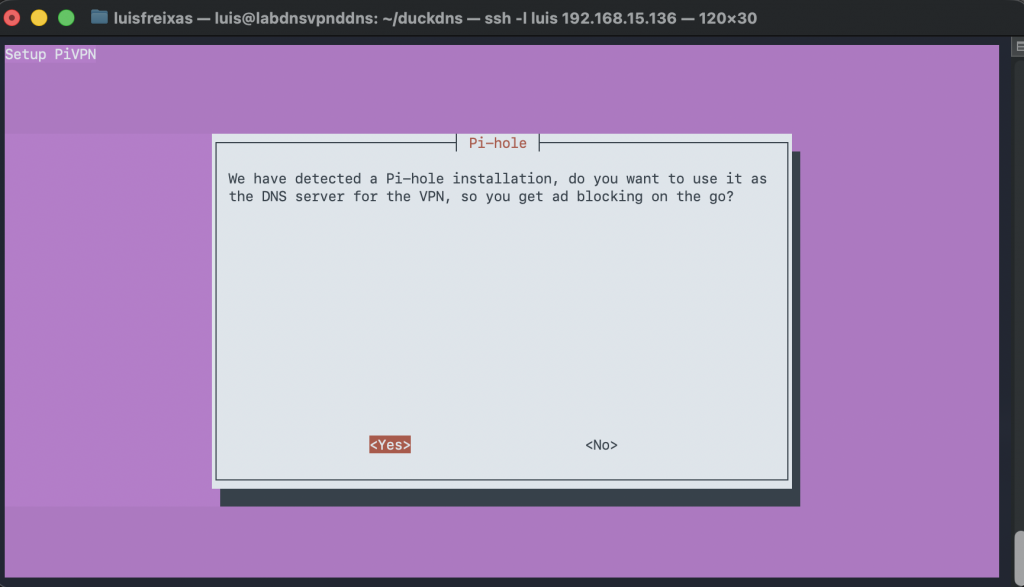
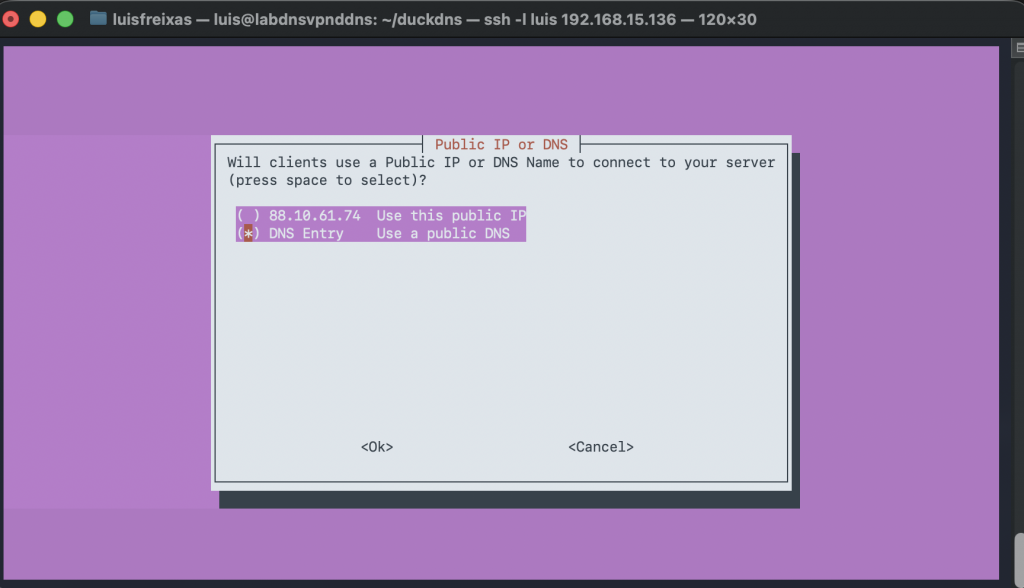
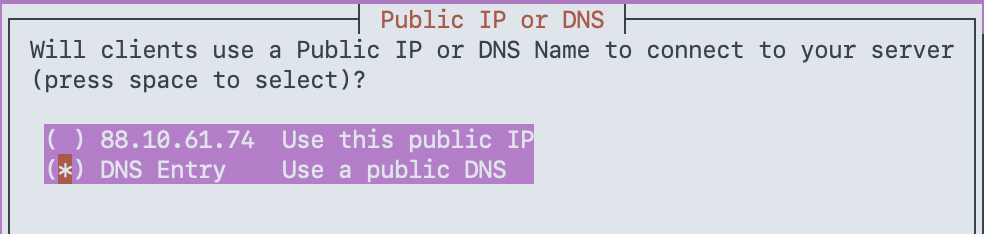
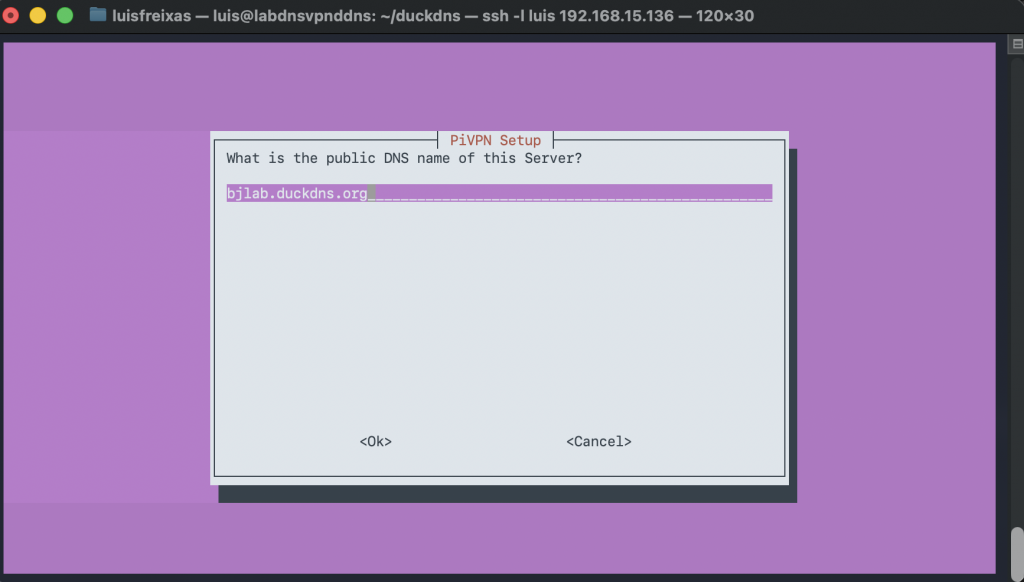
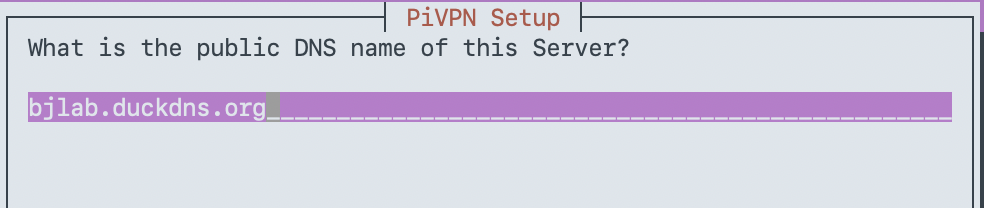
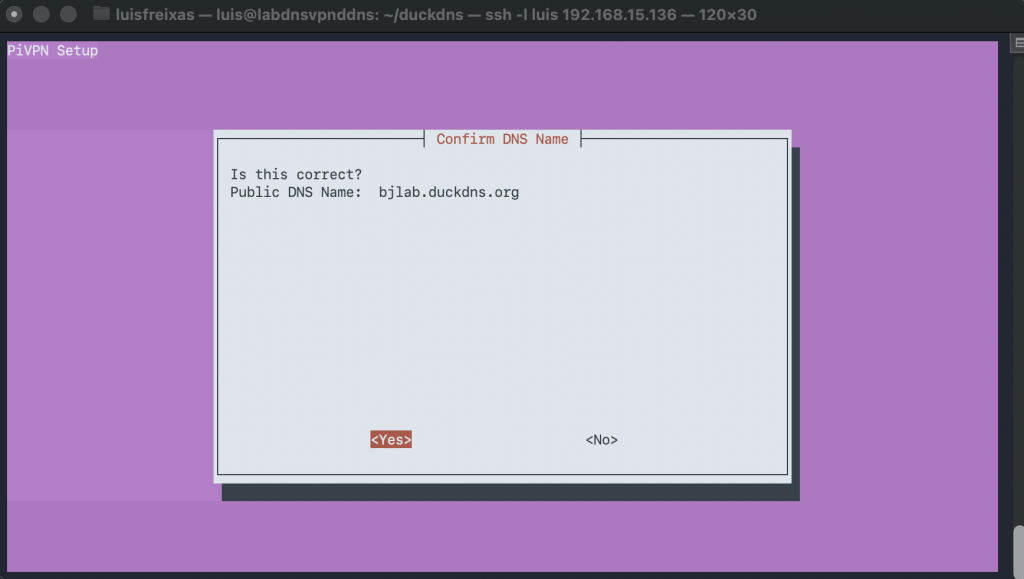
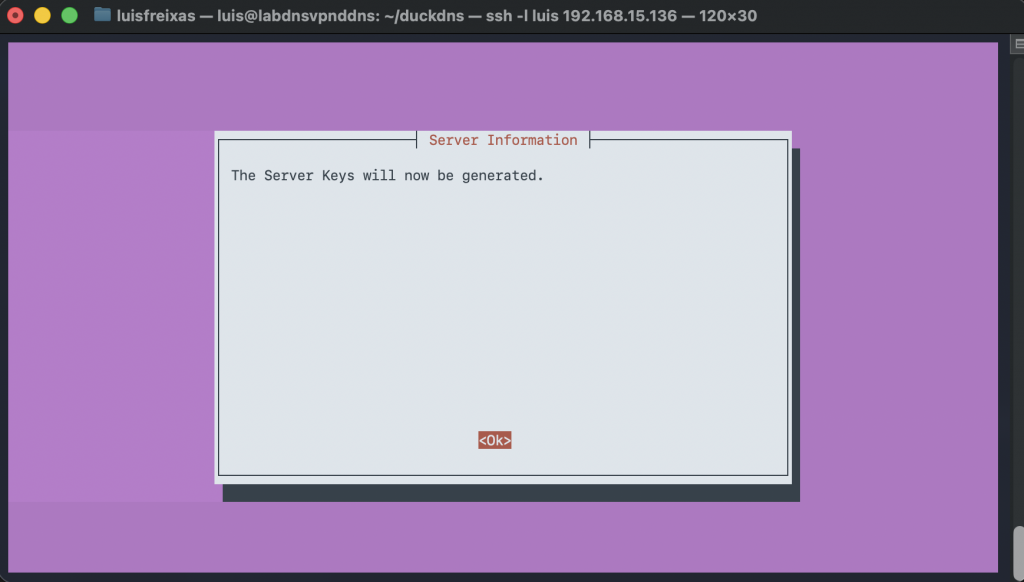
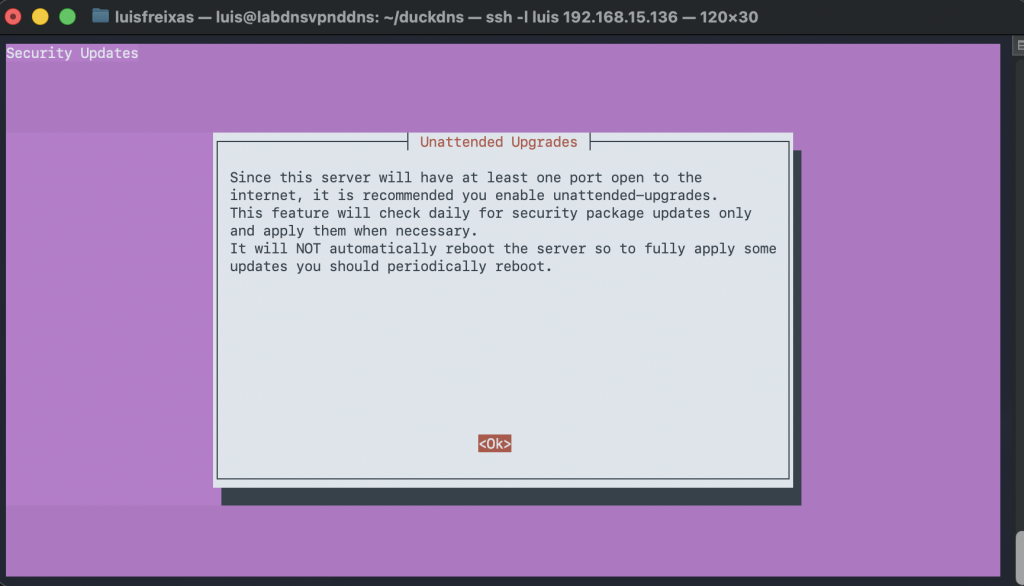
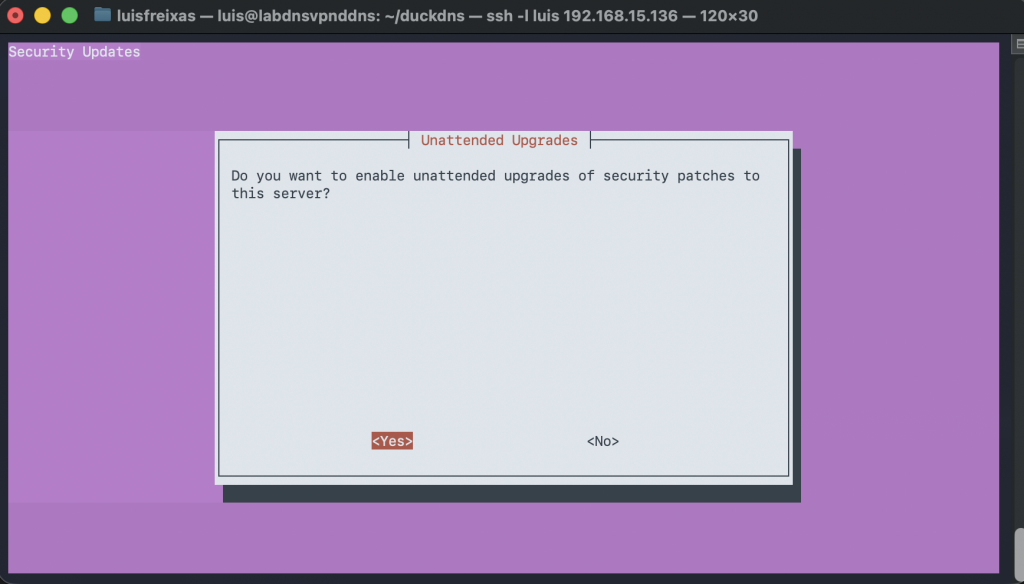
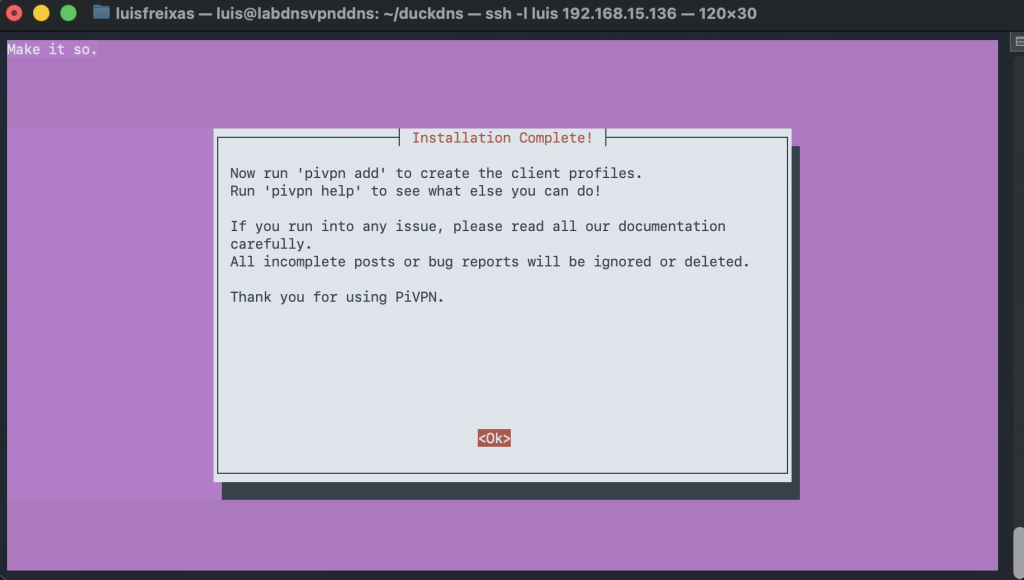
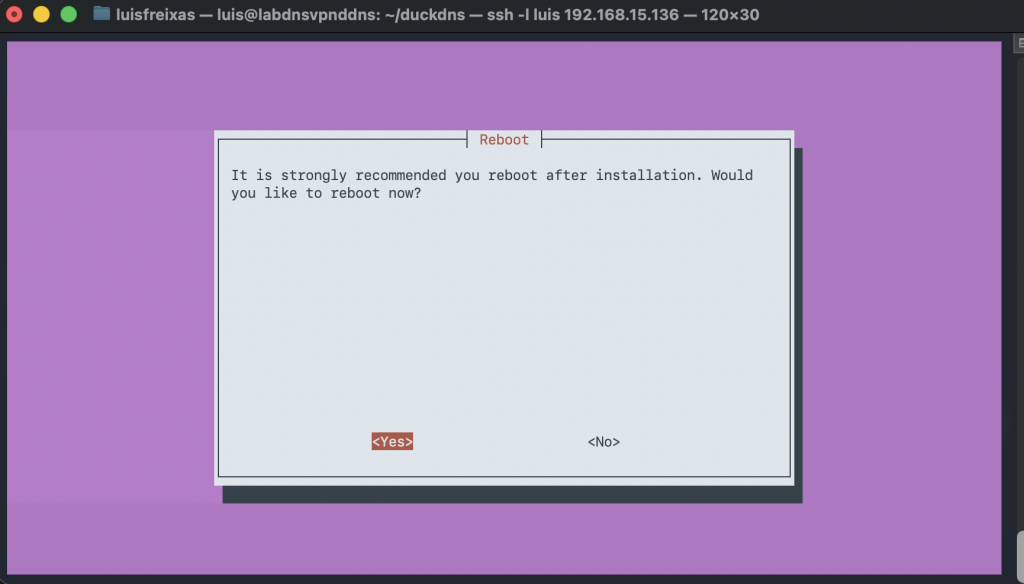
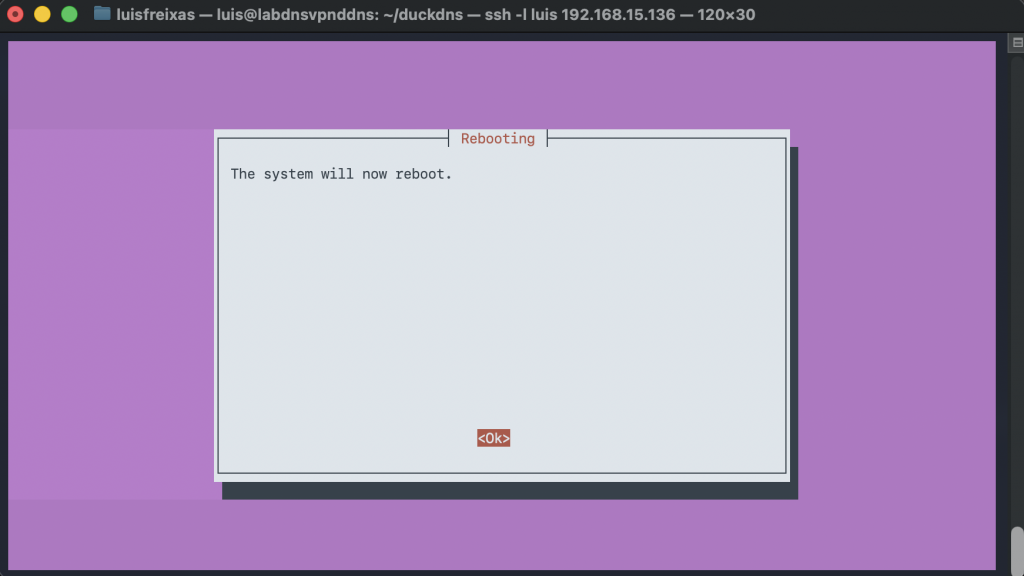
Done!
Now our server is full setup with PiHole, DuckDNS and Wireguard.
Now we need a few adjustments in PiHole and create users in WireGuard.
Important!
The Server has not a fixed IP Address, I do assign an IP address on my DHCP, if you want to do so, please setup a fix IP address into the machine.
Open your port on the router to be able to reach the VPN service from outside of your network, IP – port 51820 UDP, I normally open both, TCP and UDP
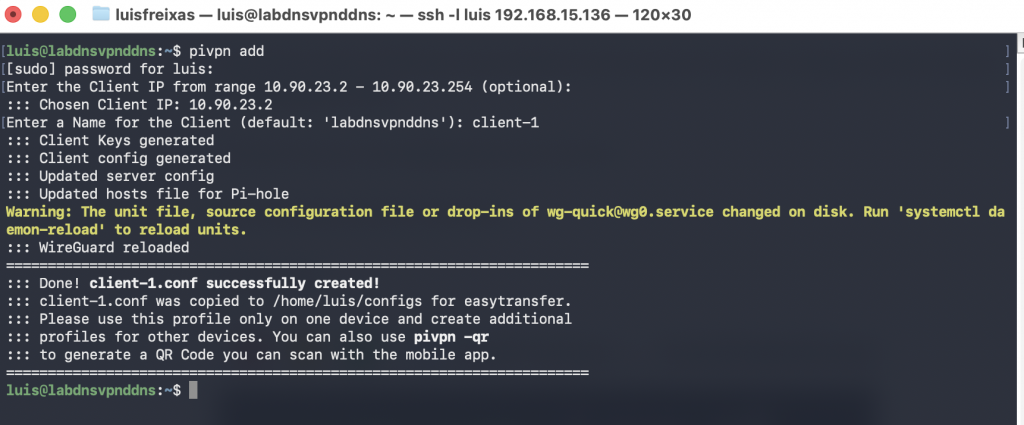
Now, lets create a VPN user, to be able to set it up into our phone / laptop, and start using our WireGuard VPN.
Connect to your new deployed server via ssh
Now, let`s execute the command:
pivpn add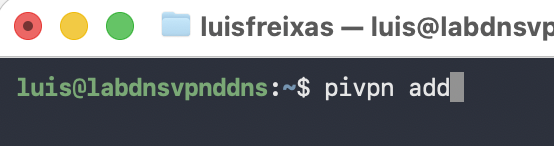
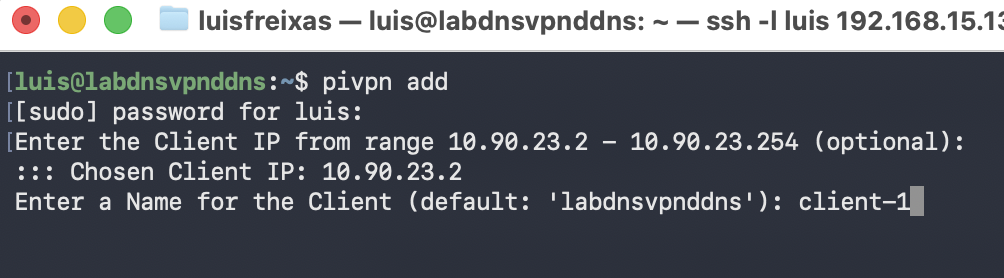
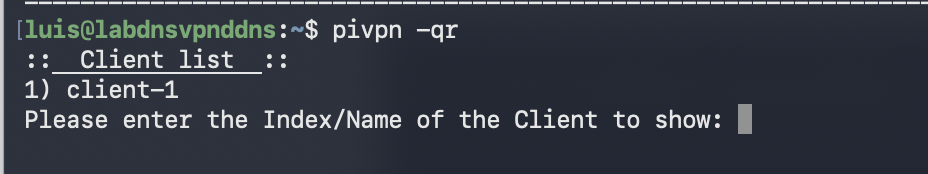
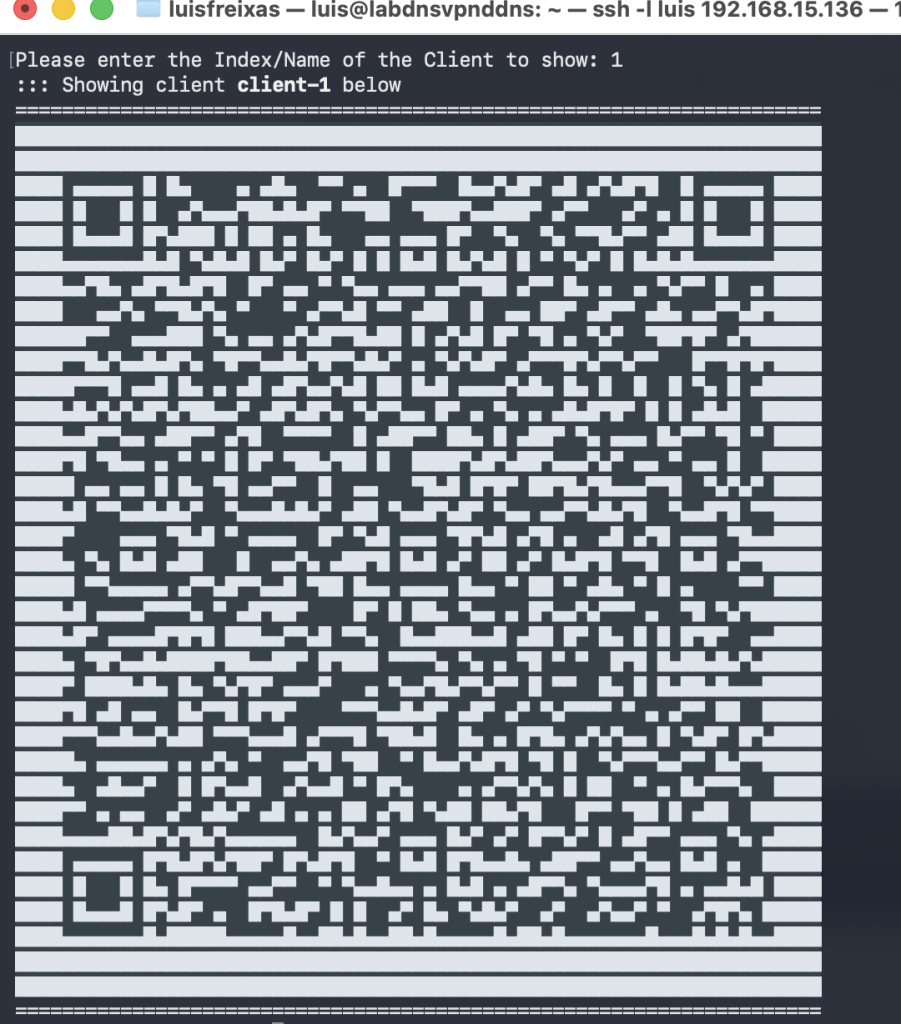


Done!
now, you have your VPN fully configure.
anua time you want to connect, simply open the app and switch the VPN to on (green)
all traffic will be back and forth the VPN.
cheers.